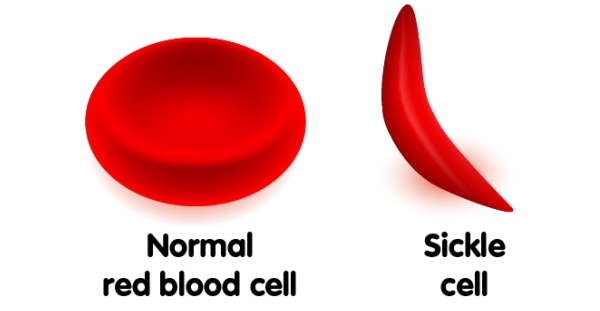
Sickle cell disease is an inherited disorder in which red blood cells (RBCs) are abnormally shaped. All the problems in sickle cell disease are due to its shape, which resembles a shaped farm tool called a sickle. Normal red blood cells are flexible and flow easily but in sickle cell disease due to its deformity, they are stiff and can get stuck in a tiny blood vessels cutting off the blood supply to nearby tissues. This abnormality can result in painful episodes, serious infections, chronic anemia, and damage to body organs. These complications can, however, vary from person to person depending on the type of sickle cell disease each has. Some people are relatively healthy and others are hospitalized frequently. Today with early diagnosis and treatment, most kids born with this disorder grow up to live relatively healthy and productive lives.